Research applications of cryogenics
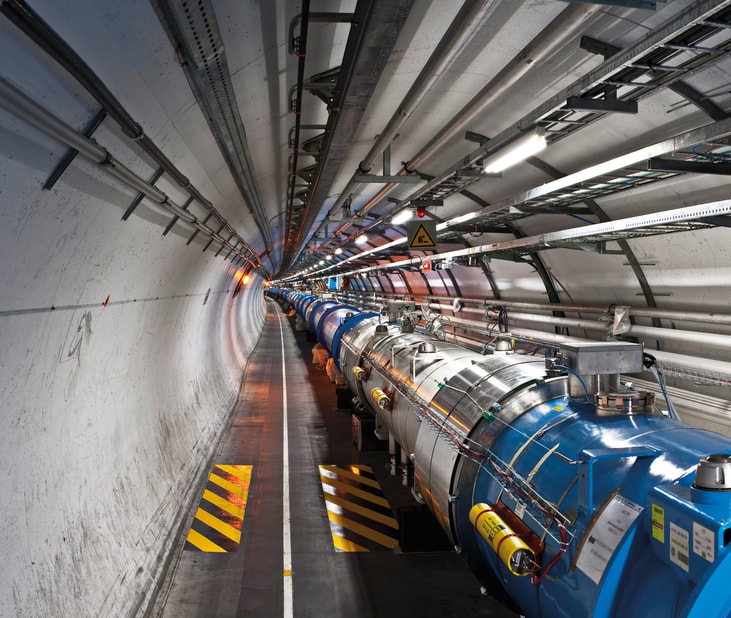
Whether used to cool superconducting magnets at CERN, as a fundamental enabler in space exploration at NASA or its role in harnessing fusion power, cryogenics is a critical enabling technology in research applications. Simply put, cryogenics is the production, management and utilisation of temperatures below those naturally found on Earth.
Cryogenic cooling of devices and material is usually achieved using mechanical refrigerators and/or a liquid cryogen such as nitrogen or helium. Lowering temperatures results in changes in the physical properties of materials – they contract, they can harden or change phase, for example gases condense to liquids, liquids freeze or solidify.
Lowering temperatures results in a lower energy state with reduced molecular vibration, which can be exploited if you are looking into molecular structures or taking high resolution pictures in different wavelengths. For this reason, samples subject to microscopic examination – to ‘see inside’ the molecular structure of the sample – are often cooled to cryogenic temperatures to get a sharper picture with less molecular vibration.
... to continue reading you must be subscribed